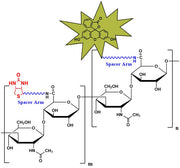
Hyaluronate Biotin - Items tagged as "Fluorescein"
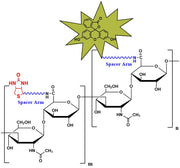
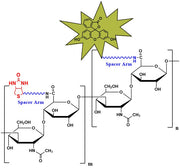
Biotinylated Hyaluronate (bHA) is a high-performance affinity probe designed for sensitive detection and characterization of hyaluronan-binding proteins. The biotin tag enables strong and specific interaction with streptavidin- or avidin-based detection systems, allowing visualization of hyaladherins such as CD44, RHAMM, cartilage link protein, aggrecan, versican, and neurocan at nanogram sensitivity (≥2 ng).
bHA performs reliably on nitrocellulose following SDS-PAGE and is ideal for electroblotting, receptor-binding analysis, extracellular matrix profiling, and studies of HA-mediated cell signaling, migration, and tissue remodeling. This reagent provides a robust, reproducible method for identifying HA-binding domains and validating HA–protein interactions in developmental, regenerative, and cancer biology research.
References
1. Biotinylated hyaluronic acid: a new tool for probing hyaluronate-receptor interactions. Bioconjug Chem., 1994, 5(4):370–372.
2. Biotinylated hyaluronic acid as a probe for identifying hyaluronic acid-binding proteins. Anal Biochem., 1995, 228(2):299–306.
3. Biotinylated hyaluronan: a versatile and highly sensitive probe capable of detecting nanogram levels of hyaluronan-binding proteins (hyaladherins) on electroblots by a novel affinity detection procedure. Electrophoresis, 1996, 17(1):205–212.
-
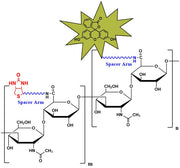
Biotinylated Hyaluronate Fluorescein, MW 5 kDa from $350.00
-
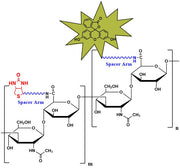
Biotinylated Hyaluronate Fluorescein, MW 10 kDa from $350.00
-
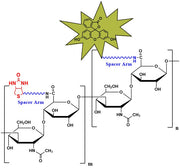
Biotinylated Hyaluronate Fluorescein, MW 50 kDa from $350.00
-
Biotinylated Hyaluronate Fluorescein, MW 100 kDa from $350.00
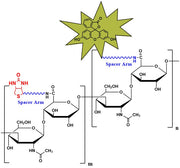
-
Biotinylated Hyaluronate Fluorescein, MW 250 kDa from $350.00
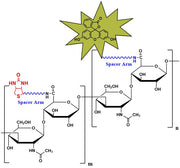
-
Biotinylated Hyaluronate Fluorescein, MW 500 kDa from $350.00
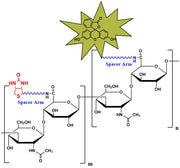
-
Biotinylated Hyaluronate Fluorescein, MW 750 kDa from $350.00
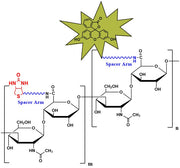
-
Biotinylated Hyaluronate Fluorescein, MW 1,000kD from $350.00
-
Biotinylated Hyaluronate Fluorescein, MW 1,500k from $350.00
-
Biotinylated Hyaluronate Fluorescein, MW 2,500kD from $350.00